Our laboratory has published a new study in Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy that clarifies the complex role of the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA) in spinal pain transmission. Anandamide is a naturally occurring lipid that binds to cannabinoid (CB1) and vanilloid (TRPV1) receptors—two key molecular players involved in pain modulation. While anandamide has long been recognized as a promising target for pain treatment, its effects in the spinal cord remained puzzling, often showing both inhibitory and excitatory actions.
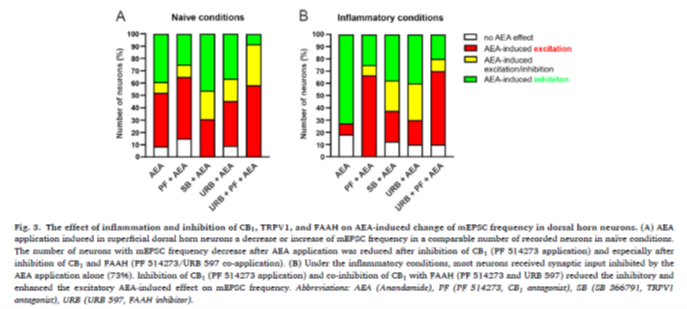
Using advanced patch-clamp electrophysiology in rat spinal cord slices, we discovered that anandamide indeed has a dual effect at the first synapses of pain pathways. In healthy conditions, anandamide produced a balanced mix of inhibitory and excitatory responses across different neuronal populations. However, during inflammation, this balance shifted dramatically: inhibitory effects became dominant, while excitatory responses nearly disappeared. Importantly, when enzymes and receptors regulating anandamide breakdown (FAAH) or signaling (CB1, TRPV1) were selectively blocked, the hidden excitatory or inhibitory effects of anandamide were revealed, demonstrating a finely tuned receptor interplay.
These results highlight that the impact of anandamide strongly depends on the physiological state of the nervous system. While exogenous (externally applied) anandamide produces complex outcomes, enhancing the body’s own production of anandamide via its precursor 20:4-NAPE appears to yield more consistent pain inhibition, as shown in our previous studies.
This research deepens our understanding of endocannabinoid signaling in pain processing and points toward targeting endogenous lipid pathways as a more promising therapeutic strategy than direct administration of anandamide. Our findings thus represent a significant step forward in the search for new and safer treatments for chronic pain.
Dual effect of anandamide on spinal nociceptive transmission in control and inflammatory conditions. Monica Pontearso , Jakub Slepicka , Anirban Bhattacharyya , Diana Spicarova , Jiri Palecek *. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 173 (2024) 116369, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116369