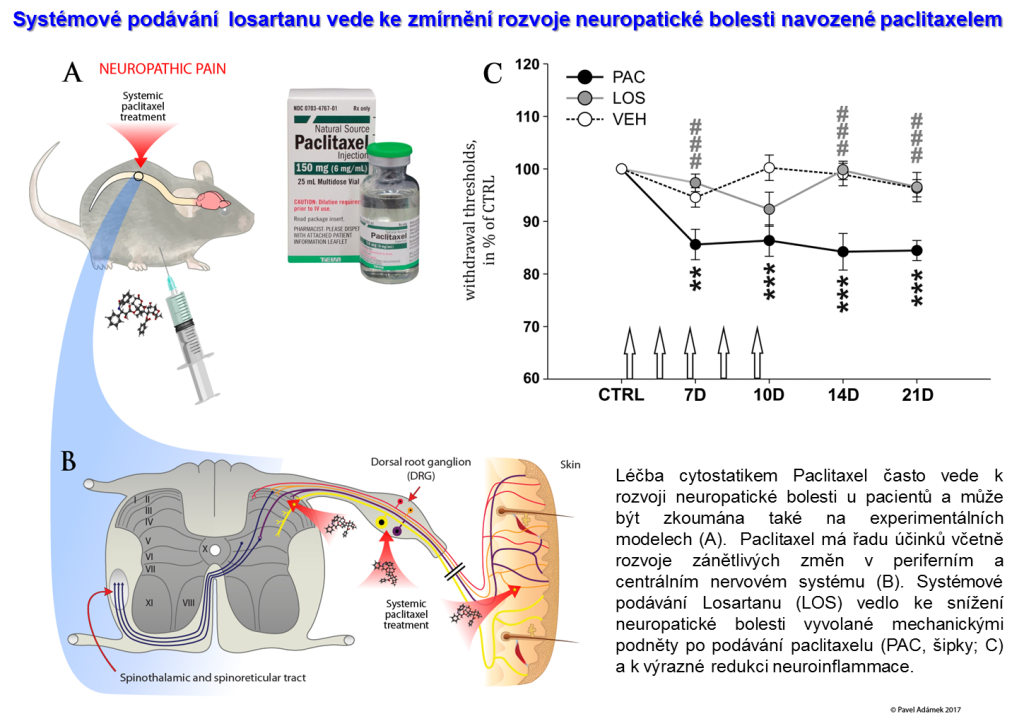
Paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients is often associated with neuropathic pain and neuroinflammation in the central and peripheral nervous system. The analgesic treatments available for this condition have numerous serious side effects and their efficacy is low. There is a great need to understand the neuropathic pain mechanisms involved in order to find new analgesic drugs. Frequently used antihypertensive drug Losartan, an angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1R) blocker, was shown to have some anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects in different disease models. In our work we have shown that systemic Losartan treatment attenuated significantly mechanical allodynia in a rodent model of Paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. Losartan also significantly reduced paclitaxel-induced neuroinflammatory changes and induced expression of pro-resolving markers (Arginase 1 and IL-10) indicating a possible shift in macrophage polarization. Considering the good safety profile of Losartan, it may be considered as a possible novel treatment strategy for patients with paclitaxel induced neuropathic pain.
Kalynovska N, Diallo M, Sotáková-Kašparová D, Palecek J Losartan attenuates neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain in paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 24, 14 (2020), 7949-7958. IF: 4.486 DOI