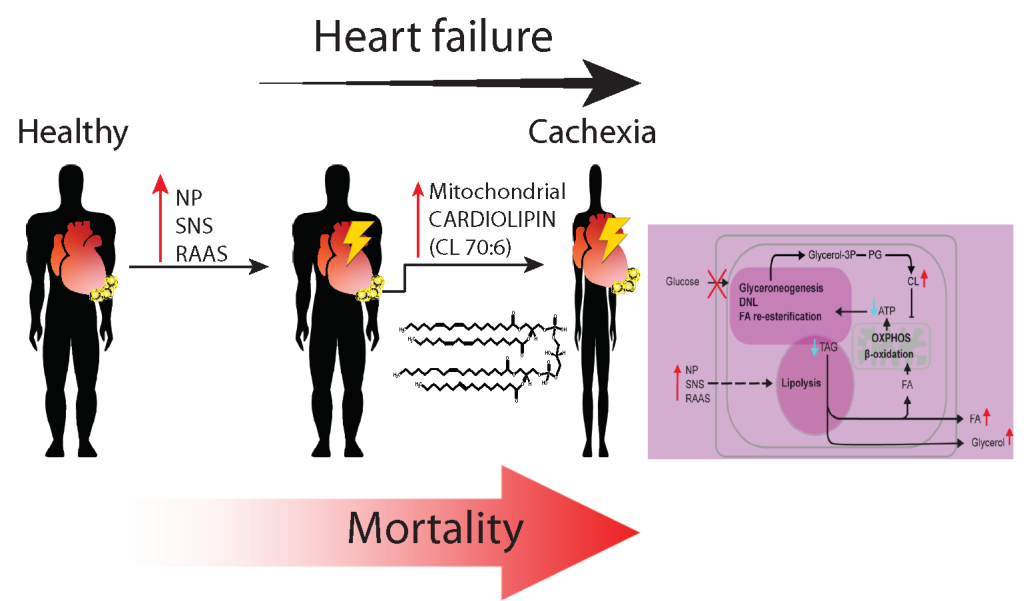
More than a half of deaths in the Czech Republic is due to the cardiovascular disease, with most of the patients suffering from heart failure (HF). Long-term prognosis of the HF-patients worsens by cachexia, which develops in a subgroup of the patients. Effective treatment of cachexia is missing. In collaboration of scientists at the Institute of Clinical and Experimental Medicine and the Institute of Physiology of the Czech Academy of Sciences in Prague, a study was conducted in advanced HF-patients (n = 52) undergoing heart transplantation. In adipose tissue from the vicinity of the diseased hearts of the cachectic patients, we have demonstrated (i) stronger neurohumoral stimulation of fatty acid (FA) release, and (ii) synthesis of unusual phospholipid cardiolipin (CL 70:6). This phospholipid may deteriorate mitochondrial functions in fat cells and accelerate wasting of the tissue. It could serve as a novel therapeutic target in cachexia.
In HF patients, lipolytic breakdown of triacylglycerols (TAG) in adipose tissue is activated in response to natriuretic peptides (NP), sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and renin-angiotensin-aldosteron system (RAAS). This results in increased release of FA and glycerol into circulation. In body weight-stable patients, the breakdown is balanced by TAG synthesis, which depends on glyceroneogenesis, de novo synthesis of FA (DNL), and FA re-esterification. These reactions require ATP, which is synthesized by oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) linked to ?-oxidation of FA in mitochondria. In the cachectic patients, lipolysis is overstimulated, in association with synthesis of CL 70:6 in adipose tissue. This lipid induces uncoupling of OXPHOS and thus inhibits synthesis of ATP, resulting in insufficient replenishment of the TAG pool in fat cells and wasting of adipose tissue.
Janovska P, Melenovsky V, Svobodova M, Havlenova T, Kratochvilova H, Haluzik M, Hoskova E, Pelikanova T, Kautzner J, Monzo L, Jurcova I, Adamcova K, Lenkova L, Buresova J, Rossmeisl M, Kuda O, Cajka T, Kopecky J. Dysregulation of epicardial adipose tissue in cachexia due to heart failure: the role of natriuretic peptides and cardiolipin. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle 2020; IF: 9.802 DOI